Automation, AI, and Geopolitics: Shaping the Future of Diagnostic Contract Manufacturing
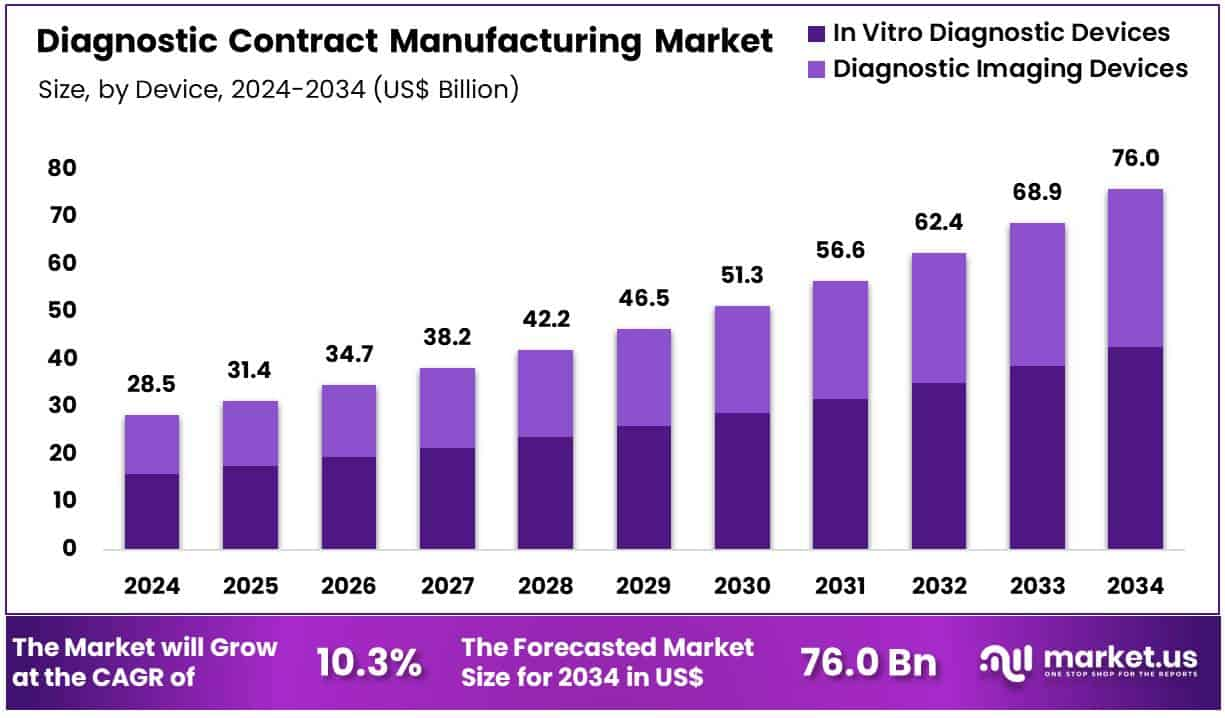
The global diagnostic contract manufacturing market is projected to reach around US$ 76.0 billion by 2034, up from US$ 28.5 billion in 2024. This growth reflects a strong CAGR of 10.3% from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America dominated the market with a 44.4% share and revenue of US$ 12.6 billion. The rising demand for cost-effective and scalable diagnostic solutions is driving innovation, especially with the integration of automation and AI in production processes.
The use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the manufacturing landscape. These technologies are enhancing precision, scalability, and operational efficiency. Advanced robotics reduce human error and accelerate routine tasks. AI-powered quality checks ensure high standards and real-time defect detection. This results in faster production and cost savings by reducing rework and manual inspections. Companies are now better positioned to meet growing demand without compromising quality or speed, especially for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices.
Automation supports seamless scalability in response to rising global healthcare needs. It helps manufacturers increase output while maintaining consistent quality. AI tools streamline production planning and reduce downtime, leading to shorter turnaround times. As IVD devices dominate the market, automation enables manufacturers to scale efficiently. This allows faster market entry and better product validation. These improvements are fostering a competitive edge and supporting long-term growth in the diagnostic contract manufacturing sector.
Macroeconomic factors also play a crucial role in shaping the market. Economic growth can increase healthcare budgets and fuel demand for diagnostics. On the other hand, downturns may cause budget cuts, delaying approvals and slowing demand. Cost fluctuations in raw materials and labor can also impact profitability. Contract manufacturers must adapt to economic shifts by improving efficiency and maintaining flexible production capabilities to stay competitive in the global market.
Geopolitical factors further affect the industry, especially through trade policies and supply chain disruptions. For example, the U.S. Biosecure Act forces companies to cut ties with certain Chinese firms by 2032. This shift is prompting U.S. companies to seek new suppliers in Europe and India. These transitions could raise production costs and cause delivery delays. To manage risks, manufacturers are diversifying suppliers, investing in regional hubs, and forming global partnerships to maintain stable operations amid uncertainty.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


