The Evolution and Precision of Modern Medical Tools

Surgeons rely on their skills, experience, and steady hands to perform life-saving procedures every single day. However, even the most talented surgeon cannot operate without the right tools. A high-quality surgical instrument acts as an extension of the surgeon's hand, allowing for precision that the human fingers alone simply cannot achieve. Whether it is a scalpel designed for the initial incision or a delicate retractor used to hold back tissue, the quality of these tools directly impacts patient outcomes.
The medical field has come a long way from the crude tools of the past. Today, technology drives the design and manufacturing of equipment used in operating rooms globally. Companies like GreyMedical® understand that innovation is not just a buzzword but a necessity in this high-stakes environment. As a privately owned medical technology company, GreyMedical® dedicates itself to excellence in crafting these essential tools. Their commitment ensures that medical professionals have reliable equipment that performs flawlessly under pressure.
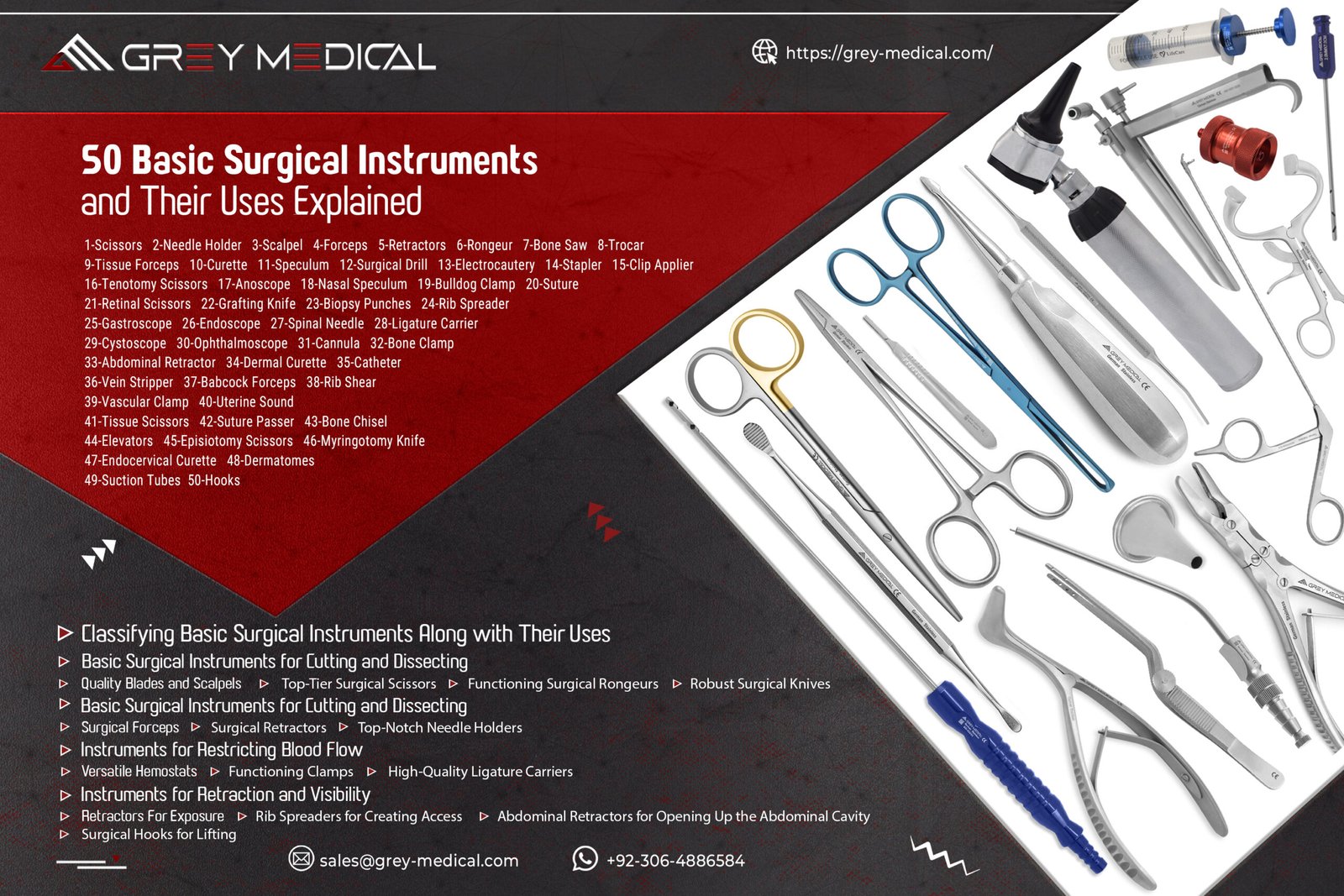
Why Quality Materials Matter in Surgery
The durability and reliability of a surgical instrument depend heavily on the materials used during its creation. Stainless steel remains the gold standard because of its resistance to corrosion and its ability to withstand the intense heat of sterilization processes. Surgeons need to know that their equipment will not fail, bend, or dull unexpectedly during a critical moment in a procedure.
Manufacturers must adhere to strict standards when sourcing these materials. A tool that rusts or degrades can cause infections or complications, which is unacceptable in modern medicine. GreyMedical® prioritizes superior craftsmanship by selecting only top-tier materials. This focus on material science ensures that every clamp, forcep, and needle holder maintains its integrity through repeated use and sterilization cycles.
Innovation in Surgical Design
Design plays a massive role in the functionality of medical tools. Ergonomics, for example, is a crucial factor that is often overlooked by the general public but deeply appreciated by medical staff. A surgeon might hold a specific surgical instrument for hours during a complex operation. If the design causes hand fatigue or cramping, it can compromise the surgeon's ability to work effectively.
Modern manufacturing techniques allow for designs that fit naturally in the hand, reducing strain and improving control. GreyMedical® invests in research to understand exactly how surgeons use these tools. By refining the weight, balance, and grip of their products, they help surgeons maintain peak performance throughout long procedures. This attention to ergonomic detail separates premium manufacturers from generic suppliers.
The Future of Medical Technology
The landscape of surgery is shifting toward minimally invasive procedures. This shift requires a new breed of tools that are smaller, more flexible, yet incredibly strong. Developing a surgical instrument for laparoscopic or robotic surgery presents unique engineering challenges. These tools must navigate tight spaces inside the human body while providing the surgeon with tactile feedback and precise control.
GreyMedical® stays ahead of these trends by embracing innovation. They recognize that the future of healthcare relies on technology that is smarter and less invasive. By continuously evolving their product lines, they ensure that hospitals and clinics have access to the latest advancements in medical technology.
Conclusion
The success of any surgery is a combination of human expertise and mechanical precision. Choosing the right surgical instrument is a decision that affects safety, recovery times, and overall procedural success. Manufacturers like GreyMedical® play a pivotal role in the healthcare ecosystem by providing the high-quality, innovative tools that modern medicine demands. As surgical techniques continue to advance, the commitment to excellence in instrument crafting will remain a cornerstone of patient care.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


