Efficient Thermal Solutions with Plate Fin Heat Exchanger Designs

In diligence where weight, space, and thermal effectiveness represent critical design constraints, the plate fin heat exchanger has established itself as a necessary technology delivering exceptional performance in compact packages. Firstly developed for aerospace operations where every gram matters, these sophisticated bias have expanded into cryogenics, natural gas processing, automotive systems, and colorful artificial processes taking effective multi-stream heat exchange. By mounting corrugated fins between flat division plates and brazing the assembly into a monolithic structure, plate fin heat exchangers achieve face area consistence exceeding 1,000 square feet per boxy, several times lesser than conventional shell and tube designs. This remarkable conciseness, combined with the capability to handle multiple process aqueducts contemporaneously, positions plate fin technology as the optimal result for demanding thermal operation challenges.
The Engineering Principles Behind Plate Fin Design
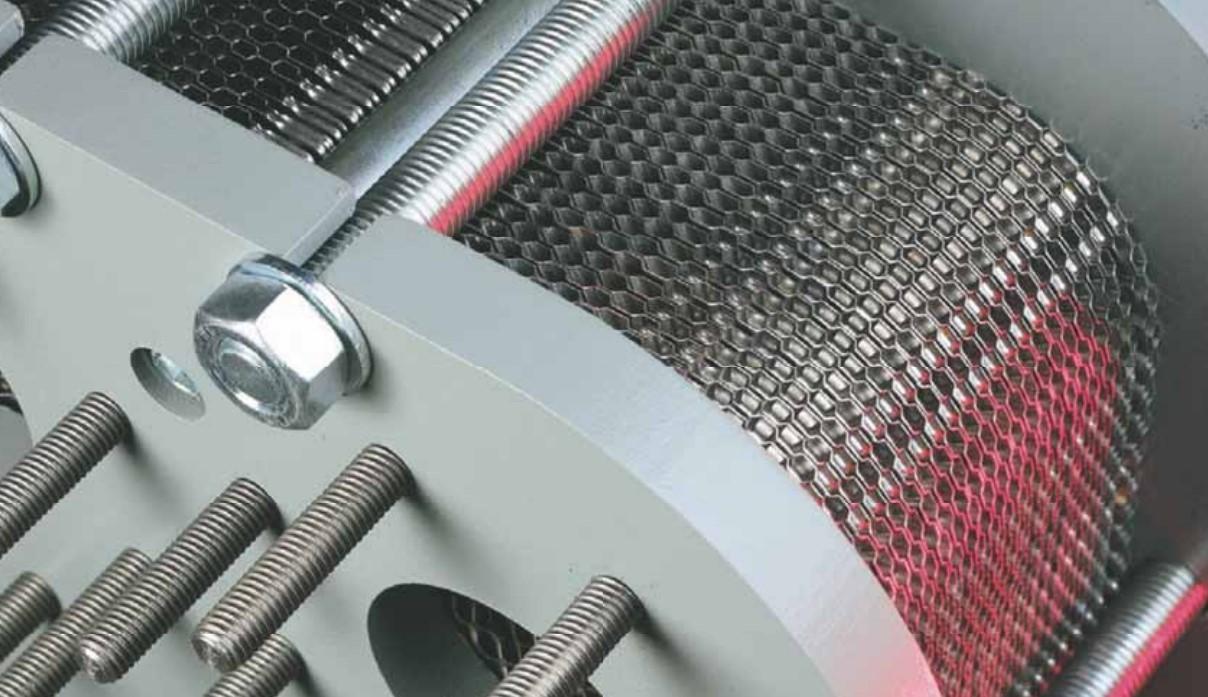
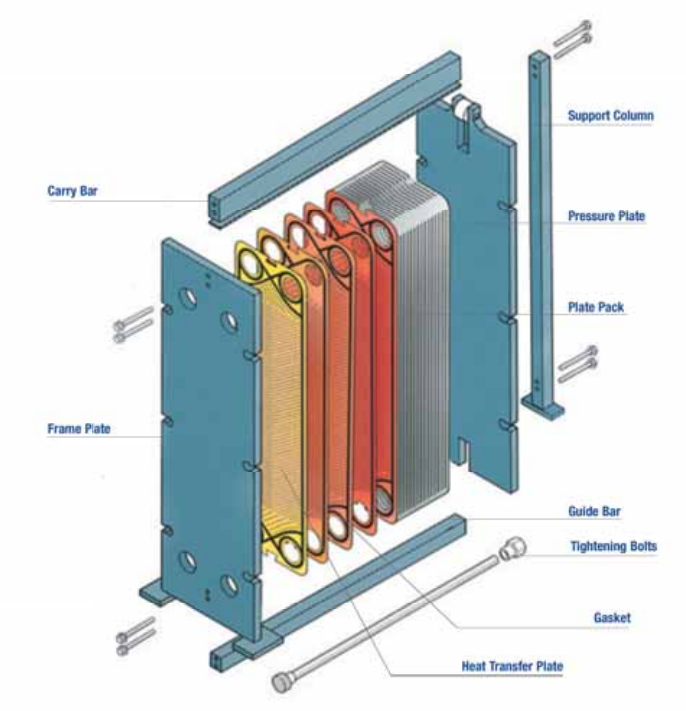
Plate fin heat exchangers correspond of interspersing layers of corrugated fins squeezed between flat division plates. The fins serve binary purposes, creating inflow passages for process fluids and dramatically adding heat transfer face area. The entire assembly undergoes vacuum brazing, creating a unified structure with excellent thermal conductivity at each interfaces and barring the sealing challenges associated with gasketed designs.
The corrugated fin figure creates multitudinous small inflow channels that promote turbulent inflow indeed at fairly low Reynolds numbers. This turbulence disrupts thermal boundary layers where heat transfer resistance concentrates, dramatically perfecting heat transfer portions compared to smooth channels. The fin patterns can be optimized for specific operations, with variations in fin viscosity, height, and figure acclimatized to balance heat transfer performance against pressure drop constraints.
The modular construction enables remarkable inflexibility in inflow arrangements. Multiple fluid aqueducts can change heat within a single compact unit, with each sluice enwrapping devoted layers within the mound. This capability proves inestimable in cryogenic air separation, natural gas liquefaction, and other processes taking heat exchange between three, four, or indeed more fluid aqueducts contemporaneously.
Superior Performance Characteristics
Exceptional conciseness and face Area viscosity
The defining advantage of plate fin heat exchangers lies in their extraordinary conciseness. Face area consistence of 800- 1,500 m ²/ m ³ allow these bias to perform thermal duties taking significantly larger vestiges with conventional outfit. In weight-sensitive operations like aircraft and aerospace systems, this conciseness directly translates to fuel savings and cargo capacity advancements. For artificial installations, reduced footmark minimizes real estate conditions and simplifies retrofits into space-constrained installations.
The high face area viscosity results from the combination of thin fins creating multitudinous small inflow channels and effective packaging that maximizes the proportion of volume devoted to heat transfer shells versus structural factors. ultramodern manufacturing ways produce fins as thin as 0.1- 0.2 millimeters, creating inflow passages that optimize the trade-off between heat transfer improvement and pressure drop.
Multi-Stream Capability
Unlike conventional two-fluid heat exchangers, plate fin designs routinely accommodate three or further process aqueducts in counterflow, crossflow, or complex arrangements optimized for specific thermal duties. Thismulti-stream capability eliminates the need for multiple separate heat exchangers, reducing outfit count, connection points, and implicit leak sources while perfecting overall process integration.
Cryogenic air separation shops illustrate this advantage, where plate fin exchangers contemporaneously cool incoming air while warming multiple product aqueducts including nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. The capability to negotiate these multiple heat exchange duties within a single compact unit dramatically simplifies factory design while perfecting thermal effectiveness through optimized temperature pinch operation.
High Thermal Effectiveness
The counterflow arrangements attainable in plate fin designs enable approach temperatures within 1- 3 °C, furnishing thermal effectiveness exceeding 95 in numerous operations. This exceptional effectiveness proves critical in cryogenic processes and waste heat recovery systems where maximizing energy transfer determines profitable viability. The capability to achieve close temperature approaches expands the range of economically feasible heat recovery openings.
Industrial Applications using Plate Fin Technology
Cryogenic Processing
Deiced natural gas( LNG) product represents one of the most demanding plate fin operations. The main cryogenic heat exchanger in an LNG factory handles massive thermal duties while cooling natural gas to roughly-160 °C for liquefaction. Plate fin designs give the effectiveness, conciseness, and multi-stream capability essential for these installations, where conventional outfit would bear prohibitive space and weight.
Air separation shops producing high-purity oxygen, nitrogen, and argon calculate considerably on plate fin exchangers. The reversing heat exchangers that remove water and carbon dioxide from feed air, along with the main heat exchangers handling product warming and feed cooling, use plate fin technology to achieve the tight temperature approaches andmulti-stream capability these processes demand.
Natural Gas Processing
Natural gas dehumidification, hydrocarbon dewpointing, and nitrogen rejection processes use plate fin exchangers for effective heat integration. The compact designs fit within coastal platforms where space limitations avert conventional outfit. The capability to handle multiple aqueducts simplifies process inflow wastes while perfecting overall energy effectiveness through optimal heat waterfall arrangements.
Automotive and Transportation
Modern vehicles decreasingly incorporate plate fin heat exchangers for machine cooling, transmission oil painting cooling, charge air cooling, and air conditioning operations. The compact, featherlight designs ameliorate vehicle effectiveness while meeting demanding thermal operation conditions. Electric vehicles particularly profit from plate fin technology for battery thermal operation systems where compact, effective heat exchange within constrained packaging spaces proves essential.
Process diligence
Chemical shops, refineries, and petrochemical installations emplace plate fin exchangers where high effectiveness, conciseness, ormulti-stream capability provides advantages over conventional designs. High-pressure hydrogen cooling, reactor effluent cooling, and colorful heat recovery operations influence plate fin technology when specific process conditions favor this approach.
Design Optimization and Material Considerations
Fin Pattern Selection
Different fin shapes optimize colorful performance parameters. Plain blockish fins give good heat transfer with moderate pressure drop, suitable for most operations. Neutralize strip fins produce advanced turbulence, enhancing heat transfer at the cost of increased pressure drop — ideal when maximizing conciseness outweighs pumping cost considerations. Perforated and louvered fins offer intermediate performance, balancing heat transfer improvement against hydraulic resistance.
Fin viscosity selection balances several contending factors. Advanced fin consistence increase face area but reduce the inflow channel size, adding pressure drop and fouling vulnerability. Lower consistence ameliorate cleanability and reduces pressure drop but immolation conciseness. Optimal selection depends on fluid parcels, fouling tendencies, and system pressure drop constraints.
Material Selection and Fabrication
Aluminum blends dominate plate fin construction due to excellent thermal conductivity, good brazability, and favorable strength-to-weight rates. Specific amalgamation selections balance erosion resistance, mechanical parcels at operating temperatures, and brazing comity. Stainless sword plate fin exchangers serve operations taking superior erosion resistance or high-temperature capability, however at penalties in thermal conductivity and manufacturing complexity.
The vacuum brazing process creates metallurgical bonds at all fin-to-plate interfaces, barring thermal contact resistance and icing structural integrity. Modern controlled-atmosphere brazing furnaces produce harmonious, high-quality joints essential for pressure constraint and thermal performance. Quality control during fabrication proves critical, as the brazed construction prevents post-fabrication internal examination or form.
Functional Considerations and Conservation
Fouling Perceptivity and Prevention
The small inflow channels that give exceptional heat transfer performance also produce susceptibility to particulate fouling. operations must insure acceptable upstream filtration and fluid cleanliness to help channel blockage. For services with necessary fouling tendencies, contrivers specify wider fin lengths and larger inflow channels, accepting modest performance penalties to maintain long-term operability.
Chemical cleaning represents the primary conservation approach for fouled plate fin exchangers. The brazed construction prevents disassembly, taking rotation of applicable cleaning results through affected passages. Proper fluid pretreatment and filtration represent the most effective fouling forestallment strategy.
Thermal Cycling and Mechanical Integrity
Cryogenic operations subject plate fin exchangers to severe thermal cycling during incipiency, arrestment, and process dislocations. The discriminational thermal expansion between factors at colorful temperatures creates mechanical stresses managed through careful design and applicable material selection. ultramodern finite element analysis tools enable detailed stress evaluation during design, icing acceptable fatigue life under anticipated operating conditions.
Partner with Thermal Engineering Experts for Optimal results
While plate fin heat exchangers offer exceptional performance for applicable operations, comprehensive thermal operation frequently requires different technologies matched to specific process conditions. Successful perpetration demands deep understanding of heat transfer principles, manufacturing capabilities, and functional considerations that come from extensive operation experience.
Kinetic Engineering provides comprehensive thermal results gauging multiple heat exchanger technologies, enabling optimal outfit selection for each unique operation. Their engineering platoon evaluates process conditions holistically, recommending technologies — whether plate fin, plate heat exchanger, shell and tube, or other designs — that best serve specific functional requirements. This technology-agnostic approach ensures guests admit outfit truly optimized for their operations rather than one- size- fits- all results.
With decades of experience across different diligence and operations, Kinetic Engineering combines theoretical knowledge with practical wisdom gained from thousands of successful installations. Their commitment to quality manufacturing, rigorous testing, and responsive specialized support provides confidence throughout outfit lifecycles from original specification through times of dependable operation. The company's client-concentrated approach emphasizes understanding unique process challenges and delivering engineered results that address real-world operating conditions.
Conclusion
Plate fin heat exchangers represent advanced thermal operation technology delivering exceptional effectiveness in remarkably compact packages. Their extraordinary face area viscosity,multi-stream capability, and high thermal effectiveness make them necessary for demanding operations in cryogenics, natural gas processing, aerospace, and colorful artificial processes. While the small inflow channels bear careful attention to fluid cleanliness and fouling forestallment, proper design and operation deliver sustained high performance throughout outfit's lifecycles. Understanding the principles, capabilities, and limitations of plate fin technology enables masterminds to apply this important tool where its unique advantages give maximum value. As diligence continue prioritizing energy effectiveness, space optimization, and weight reduction, plate fin heat exchangers will expand their formerly significant part in ultramodern thermal operation, furnishing elegant results to decreasingly demanding heat transfer challenges across different operations and diligence worldwide.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


