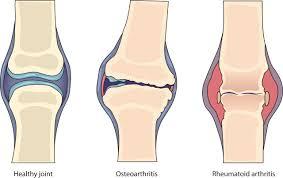
Arthritis is a broad term that refers to inflammation of the joints. Among the many types, Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) are the most common. Although they share some symptoms, such as joint pain and stiffness, they are fundamentally different in their causes, progression, and treatment approaches. Understanding these differences is key to proper management and improved quality of life.
Carticlas tablets are a cutting-edge dietary supplement formulated to promote joint health, reduce inflammation, and support overall well-being. They are designed to address the common issues associated with aging, high physical activity, and other factors that affect joint and bone health.
What Is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Osteoarthritis, often called the “wear-and-tear arthritis,” occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones gradually breaks down. This leads to bones rubbing against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Common symptoms of OA include:
-
Joint pain that worsens with movement
-
Stiffness, especially after waking up or inactivity
-
Swelling in the affected joints
-
Loss of flexibility
-
Bone spurs (extra bits of bone around joints)
Risk factors for OA:
-
Aging (most common in people over 50)
-
Previous joint injuries
-
Obesity, which puts extra stress on weight-bearing joints
-
Genetic predisposition
OA most often affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the lining of the joints (synovium). This causes painful inflammation that can eventually damage cartilage and bone. Unlike OA, RA can also affect other systems, such as the skin, eyes, heart, and lungs.
Common symptoms of RA include:
-
Joint pain and swelling, often symmetrical (affecting both sides of the body)
-
Warmth and redness around joints
-
Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
-
Fatigue and low-grade fever
-
In advanced cases, joint deformities
Risk factors for RA:
-
Genetics and family history
-
Being female (RA affects women more than men)
-
Smoking, which increases the likelihood of developing RA
-
Environmental triggers
RA typically affects smaller joints first—such as those in the hands and feet—before spreading to larger joints.
Key Differences Between OA and RA
-
Cause
-
OA: Mechanical wear-and-tear of cartilage.
-
RA: Autoimmune reaction attacking the joints.
-
-
Onset of Symptoms
-
OA: Gradual development over years.
-
RA: Can develop relatively quickly, within weeks or months.
-
-
Joint Pattern
-
OA: Often affects individual joints (knees, hips).
-
RA: Usually affects joints symmetrically (both hands, both knees).
-
-
Morning Stiffness
-
OA: Lasts less than 30 minutes.
-
RA: Can last longer than 30–60 minutes.
-
-
Systemic Involvement
-
OA: Localized to joints.
-
RA: Can affect other organs beyond joints.
-
Treatment Approaches
For Osteoarthritis (OA):
-
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
-
Physical therapy and strengthening exercises
-
Weight management to reduce joint stress
-
In severe cases, joint replacement surgery
For Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
-
Biologic therapies to control immune response
-
Corticosteroids for flare-ups
-
Physical therapy to maintain mobility
Lifestyle changes, such as balanced nutrition, exercise, stress management, and quitting smoking, can benefit both OA and RA patients.
Final Thoughts
While both OA and RA cause joint pain and stiffness, they are very different conditions. Osteoarthritis is primarily a degenerative joint disease due to aging or injury, whereas Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disorder with widespread effects.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in managing both conditions. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can maintain mobility, reduce pain, and improve their quality of life.
👉 Do you want me to also create a short, SEO-friendly title (59 characters) and meta description for this blog?